Archaeology
The ever-evolving Hagia Sophia
Ponte Vecchio view, after the Germans left Florence in 1944

Veduta dei danni inferti dai tedeschi prima della ritirata da Firenze.
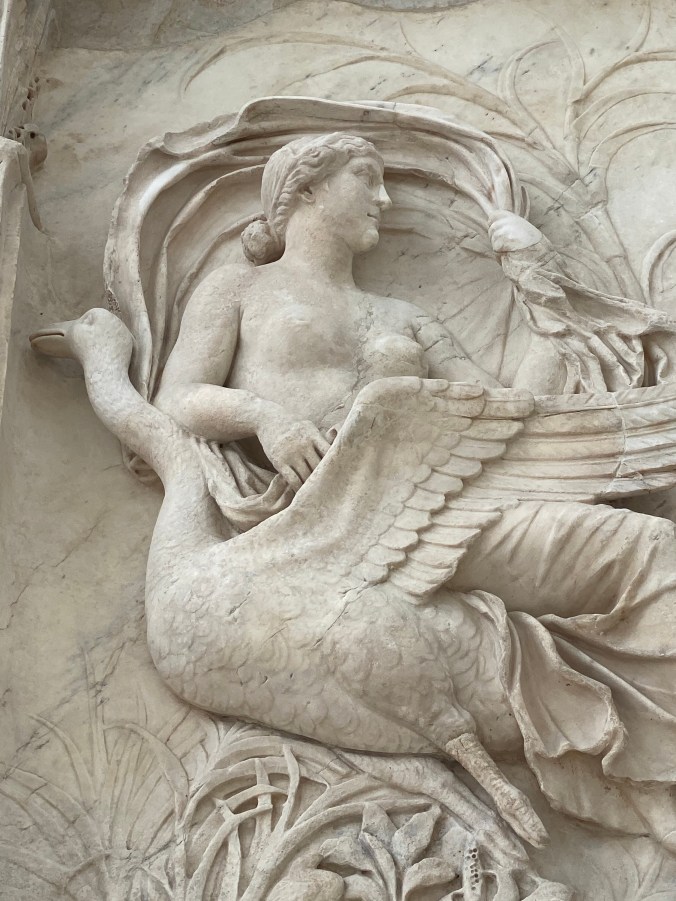
The Ara Pacis, Rome
One of the loveliest, and smallest, museums I like to visit in Rome is the Ara Pacis. On my recent visit to Rome, I enjoyed this almost empty museum.








My video below captures the interior of the monument, just before a guard told me I couldn’t make a video.















Keeping up appearances: Orsanmichele
It isn’t easy keeping a nearly 700 year old structure looking fresh. But, Florence does an amazing job. This week, Orsanmichele was getting a sprucing up.


The Pantheon, Rome
No visit to Rome is complete in my book without stopping in to visit this august structure. Without the normal crowds, my visit was superb!


Raphael is on my mind, for I will be visiting the Raphael exhibition the following day. Here is his tomb inside the Pantheon.














Piazza Navona, Rome
Rome in July of 2020, after Covid has cleared the streets.







The Trevi Fountain, without the crowds
July 2020. Rome is beautiful and accessible with fewer people.




The fountains of Rome: Fontana dell’ Aqua Felice
On a recent July visit to the Eternal City, I was wandering around the Quirinale section of Rome on a vert hot day and was delighted to bump into a number of glorious fountains. I considered hopping into a couple of them, just to cool off. I didn’t, but I dipped my hands into any that were reachable. It helped.
I was in Rome specifically to enjoy it while the hordes of tourists are not yet present. The aftermath of the Covid pandemic has cleared the streets and galleries of the usual mass tourism. I typically don’t travel to Italian cities in the summer, for I am not a fan of intense sun and heat. But, the opportunity to see the landmarks with no crowds drew me. Plus, after months of lock down, I was itching to get out and about.

Wandering around Rome, one of the first of these very interesting watery landmarks I encountered was the monumental wall fountain known as the Fontana dell’Acqua Felice, aka the Fountain of Moses. This fountain marks the end of a Roman era aqueduct, the Alessandrina, which was restored by Pope Sixtus V. It was designed by Domenico Fontana and built in 1585-88.

When Pope Sixtus V (born Felice Peretti) began his reign in 1585, only one of the ancient Roman aqueducts, the Aqua Vergine, was still bringing water to Rome.
It is hard to believe, but anyone in Rome who wanted clean drinking water had to go to the single fountain near the site of today’s Trevi Fountain.
Pope Sixtus took on the responsibility of restoring other aqueducts, including the Acqua Alessandrina, which he modestly renamed Acqua Felice after himself. The Alessandrina was named for the Roman emperor Alexander Severus, under whose reign it had been built starting around 222 A.D., using water from springs present in the “Prati dell’osteria” and Pantanella, not far from Palestrina.
Before assuming that pope’s intention was wholly altruistic, however, we must keep in mind that part of his goal was to supply water to the city districts rising in the Viminale and Quirinale hills, particularly since his sumptuous and vast Villa Montalto stretched over both. To this end, the Alexandrain aqueduct was restored,

The aqua Felice fountain was the first new monumental wall fountain constructed in Rome since antiquity.

Architect/engineer Domenico Fontana constructed the fountain in the form of an ancient Roman triumphal arch. It featured, as ancient Roman fountains did, an inscription honoring its builder, Pope Sixtus, beneath angels holding the papal coat of arms.
The central arch features a large statue of Moses, created in 1588 by Leonardo Sormani and Prospero da Brescia. Why Moses, you might ask, for a Roman fountain?
The pope, as both religious and political ruler of the papal states, purposely identified with Moses: for as Moses struck a rock to cause water to flow (Exodus 17:5-7), Pope Sixtus likewise caused water to flow.
The left bas-relief panel by Giovanni Battista della Porta, may depict alternatively depict miracles by Moses at Marah, where Moses removed the bitterness of the barely potable water of a spring in Sinai, or as a depiction of Aaron.
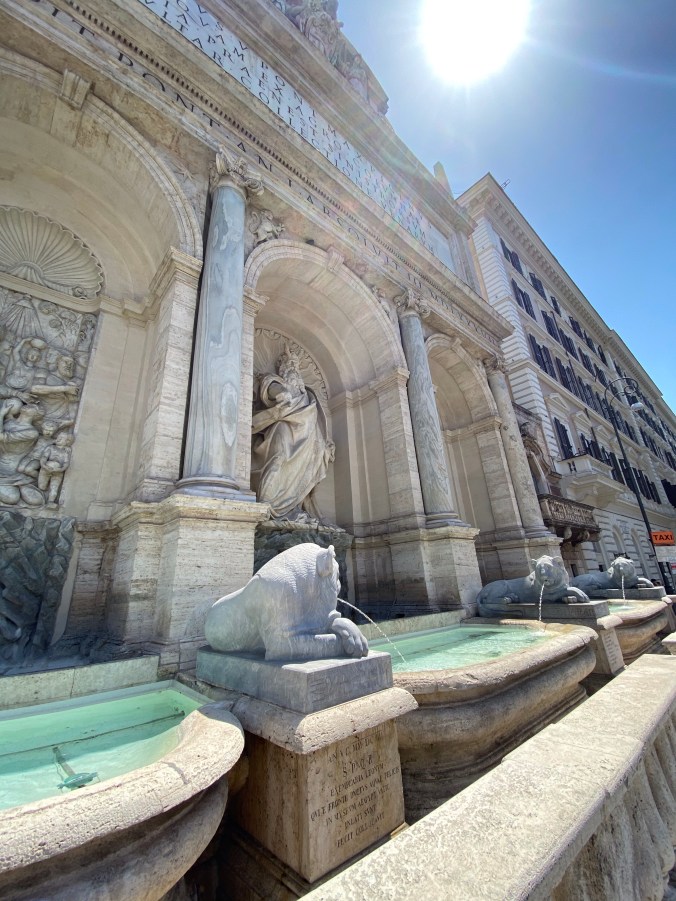

The bas-relief to the right, by Flaminio Vacca and Pietro Paolo Olivieri, has been identified as Joshua, but others claim the relief references Gideon in Judges 7:5, as evidenced by soldier’s gear and animals lapping water. It could also be founding of the ancient Roman Acqua Alessandrina by emperor Septimus Severus, based upon the Roman attire of the soldiers. In any case, the imagery speaks to the feat of restoring the aqueduct being compared to the achievements of ancient Rome. It refers to the restoration of the former glory of the city.


The iconography of the sculptures beneath the arches mingles both biblical and political motifs.

Water flows from the statues into basins, where four lions spout water. These lions were originally ancient Egyptian sculptures, but they have been replaced now with copies. The antique lion sculptures were once a part of a monumental fountain dedicated to Marcus Agrippa in front of the Roman Pantheon. The columns flanking the arches are also said to have derived from that structure.

For the truly intrepid reader, the following interesting information comes from the Italian wikipedia and translated by Google Translate: https://it.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fontana_dell’Acqua_Felice
On May 28, 1585, in the same month of his elevation to the pontificate, Sixtus V purchased the land where those waters flowed from Marzio Colonna for the sum of 25,000 scudi. The project for conveying the water was entrusted to Matteo Bortolani, from Città di Castello, “expert architect of that time and in such paid business”, whose faulty calculations on the slope of the aqueduct pipes prevented the regular flow of water. These miscalculations, in fact, “made itself retrograde to its design, going back”. The water apparently flowed backwards.
After having spent 100,000 scudi in vain, the pope then entrusted the project to the architect Giovanni Fontana, brother of the better known Domenico. Fontana wrote, in his report on the works, that he was “forced to seek other waters from those mountains of greater level, making many thousands of keys, as long as in number of 50 and more places I found the desired amount of water, otherwise the said Pontiff had thrown away all the expenses,” which would eventually add up to almost 300,000 scudi.
In August 1586, Camilla Peretti brought to the pope the bottle with the first water from the new pipes which, analyzed by the pharmacists of Castel Sant’Angelo, was found – perhaps with some courtesy – to be the best of the drinking water flowing in Rome. In October, the fountains of his Villa Montalto, on the Viminale, spurted with the new water and at the end of the year Felice water reached the highest of the Roman hills, the Quirinale, so that work could be started on the fountain of Montecavallo, between the two colossal statues of the brothers Castore and Polluce, and for the fountain of Santa Susanna, in the current Piazza San Bernardo.
The fountain was built near the vineyard of Orazio and Matteo Panzani in Termini (ie at the baths of Diocletian ), next to the monumental rusticated portal of the villa, perhaps the work of Jacopo Del Duca. A small eighteenth-century façade was later built between the portal and the fountain; the portal was dismantled in 1907 for the construction of the Grand Hotel and was reassembled in 1911 in room VIII of the baths of Diocletian, in the National Roman Museum.
Here, although the work was still unfinished, the monumental exhibition designed by Giovanni Fontana himself was finally inaugurated on 15 June 1587, with three empty niches and punctuated by four Ionic columns, two of cipollino marble and two of gray breccia, in correspondence with four Egyptian-style stylized lions that pour water from the mouth into three adjacent rectangular tanks. The columns hold the architrave on which the attic is topped, surmounted by a shrine containing the papal coat of arms supported by two angels and flanked by two small obelisks (added two years after the inauguration). To protect the tanks is a travertine balustrade from a building erected under the pontificate of Pius IV .
The inscription placed under the large frame of the attic reads:
Inscriptions on the fountain
IOANNES FONTANA ARCHITECTVS EX PAGO MILI AGRI NOVOCOMENSIS AQVAM FELICEM ADDVXIT
while the self-celebratory inscription of the pontiff on the huge attic (whose height, including the shrine with the coat of arms, is almost half of the entire monument) attests that
( LATIN )
SISTVS V PONT. MAX. PICENVS
AQVAM EX AGRO COLVMNAE
VIA PRAENST. SINISTRORSVM
MVLTAR. COLLECTION VENARVM
DVCTV SINVOSO AT RECEPTACVLO
MIL. XX A CAPITE XXI ADDVXIT
FELICEMQ. DE NOMINE ANTE PONT. DIXIT
(English)
“Pope Sixtus V Piceno, from the agro Colonna on the left of via Prenestina, collected water from many springs from the twentieth to the twenty-first mile, for a sinuous line and called it Felice from the name he had before becoming pope.”
Immediately under another inscription specifies that
( LA )
« COEPIT PONT. AN. I ABSOLVIT III MDLXXXVII »
(English) «(The work) began in the first and ended in the third year of the pontificate 1587.»
Much of the travertine comes from the nearby thermal baths of Diocletian, “looted” for the occasion. The original lions, two of porphyry and two of light marble – bearing the inscription of the pharaoh Nectanebo I – came from the Pantheon, where they were found, together with other ornaments, in the excavations conducted during the pontificate of Pope Eugene IV ( 1431 – 1439 ), and from the central entrance of the basilica of San Giovanni in Lateran, where they supported the columns next to the door.
Transferred to the Vatican Museums under Pope Gregory XVI ( 1831 -1846 ) to remove them from possible damage, they were replaced by copies made by the sculptor Adamo Tadolini.
The “ridiculous” Moses:
In the central niche is Moses which indicates the waters miraculously flowed from the rock, by Leonardo Sormani , with the collaboration of Prospero Antichi, called Bresciano, to whom the exclusivity of the work was long attributed, with the false legend that, because of the shame he felt for the ugliness of the statue, he would have committed suicide. In addition to the anachronism of the presence of the Tables of the Law, which Moses had not yet received at the time of the miracle of the waters, the statue, although it intends to refer to Michelangelo’s models, is squat and emphatic, so much so as to be called by the Romans the ” Ridiculous Moses “and be subject to pasquinate such as:
I look with a grim eye
the water that flows to the feet
thinking horrified
to the damage that he did to him
a stunned sculptor
or also
Fresh water is good and the fountain is beautiful
With that monster above, however, it is no longer that
O you, Sixtus, who cares so much for your word
The new Michelangelo hangs himself by the throat
In the side niches there are two high reliefs, depicting biblical episodes connected with water: on the left, Aaron leads the Jewish people to the water that came out of the desert, by Giovan Battista Della Porta and on the right the Gideon chooses the soldiers observing their way of drinking by Flaminio Vacca and Pietro Paolo Olivieri, authors also of the angels holding the coat of arms of Sixtus V.
It was the first of the Roman fountains purposely built as water exhibits, but its grandeur does not redeem the disharmony between the frontispiece and crowning, the meanness of the two small obelisks and, of course, the unhappy success of the statue of Moses, which also of the fountain it had to be the main artistic reference, as well as the two lateral reliefs. It is not improbable that among the causes of the modest quality of the monument there could also be a certain hurry that the pope imposed on Fontana for the conclusion of the work. Such a hurry could also justify, among other things, both the confusion already existing in the same documents of the time that define the panel of the right niche also as Joshua who leads the Jews across the Jordan, an event very different from what it actually appears to be, is the use of a balustrade taken from a previous monument from the time of Pope Pius I, without even bothering to cancel or cover its name.
The fountain was recently restored thanks to the contribution of the Fendi company : the works were completed on 26 November 2019.
The Florentine church and convent of Carmelite St. Maria Maddalena de’ Pazzi




Santa Maria Maddalena dei Pazzi is a Renaissance-style Roman Catholic church and a former convent located in Borgo Pinti in central Florence.
The Pazzi name was added after the Carmelite order nun Maria Maddalena de’ Pazzi, canonized in 1669, whose family patronized the church. The original convent had been dedicated to St. Mary Magdalen delle Convertite, the patron of once-fallen, now converted women. The Cistercian order from Badia a Settimo took control of the site in 1332 and moved to it in 1442, while the convent was transferred to San Donato in Polverosa. However, the church and chapter house were rebuilt between 1481 and 1500, with initial designs in 1492 by Giuliano da Sangallo.
The 13th-century interiors were redecorated in the 17th and early 18th centuries, which removed the altarpieces by masters such as Botticelli, Perugino, Lorenzo di Credi, Domenico Ghirlandaio, and Raffaellino del Garbo. They were replaced by new ones from minor masters such as Carlo Portelli, Alfonso Boschi, Domenico Puligo, Santi di Tito, and Francesco Curradi. In the chapter house is a fresco divided into three lunettes of the Crucifixion and Saints (1493–96) by Pietro Perugino, commissioned by Dionisio and Giovanna Pucci.
The first chapel to the right of the entrance is the Cappella del Giglio (Chapel of St. Mary of the Lily) frescoed with depictions of Saints Filippo Neri, Bernard, Nereo, and Achilleo by the studio of Bernardino Poccetti, with an altarpiece by Domenico Passignano. The fourth chapel on the right has a stained glass window by Isabella, the daughter of Georges Henri Rouault. The choir chapel originally contained a fresco by Domenico Ghirlandaio but was rebuilt from 1685 to 1701 by Ciro Ferri and Pier Francesco Silvani. Ferri painted the altarpiece and Luca Giordano the flanking pieces. The statues of Penitence and Faith on the right were sculpted by Innocenzo Spinazzi, while Innocence and Religion on the left by Giovanni Monatauti. The bronze reliefs on the altar were made by Massimiliano Soldani-Benzi.
The interior also contains works by Giovanni and Cosimo Bizzelli, Jacopo Chiavistelli, Ottavio Vannini, Cosimo Rosselli, Cosimo Gamberucci, Leonardo del Tasso, Giuseppe Servolini, and Giuseppe Piattoli.
This church is home to the Congregazione Agostiniani dell’Assunzione.
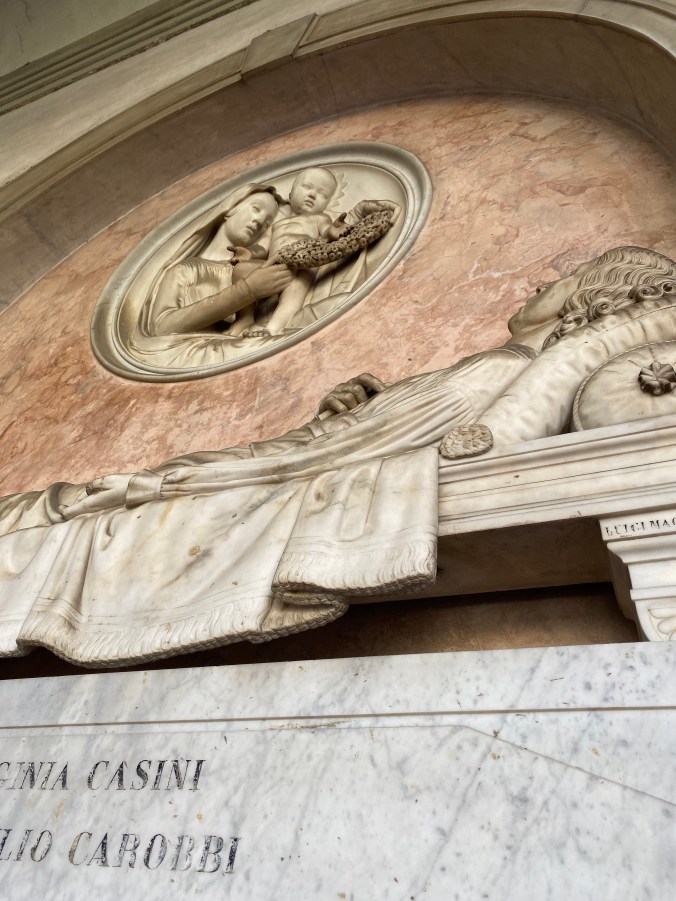
The cortile has some interesting funerary monuments:

Neoclassical sculptures of this type are rarely signed by the artist. I found this interesting signature carved onto the left of the funerary bier.


You must be logged in to post a comment.